- Главная
-
Продукция
-
Протектор резьбы API
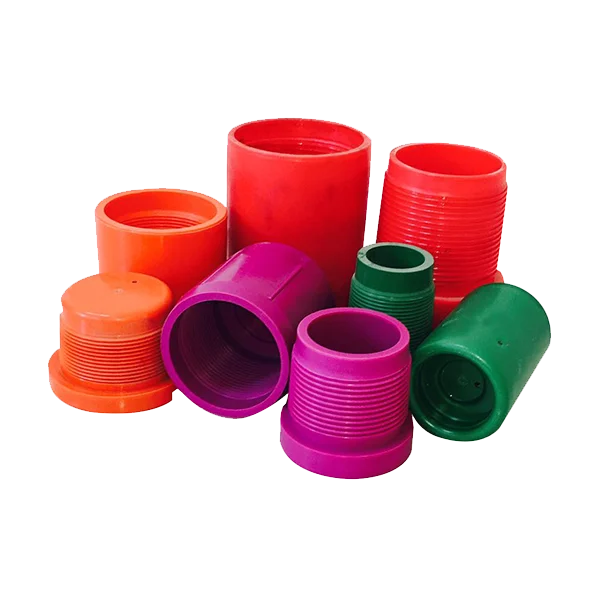

-
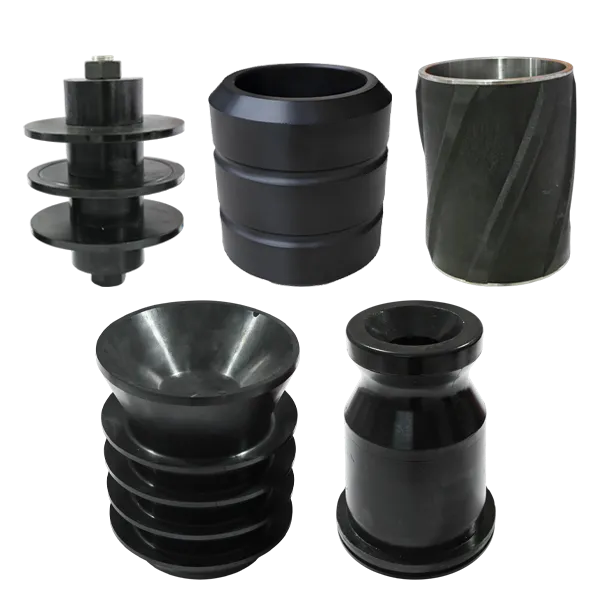
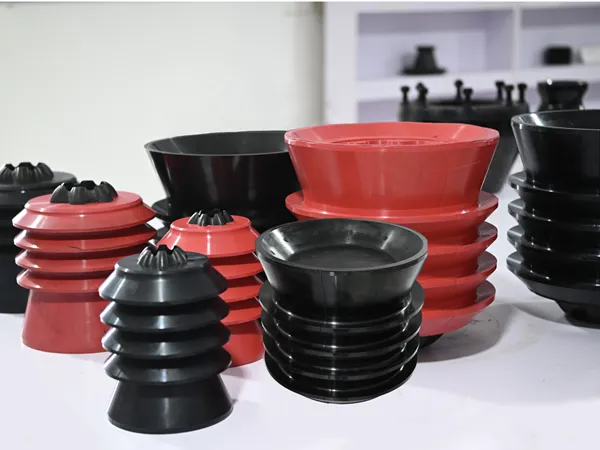
Mud Pump Accessories
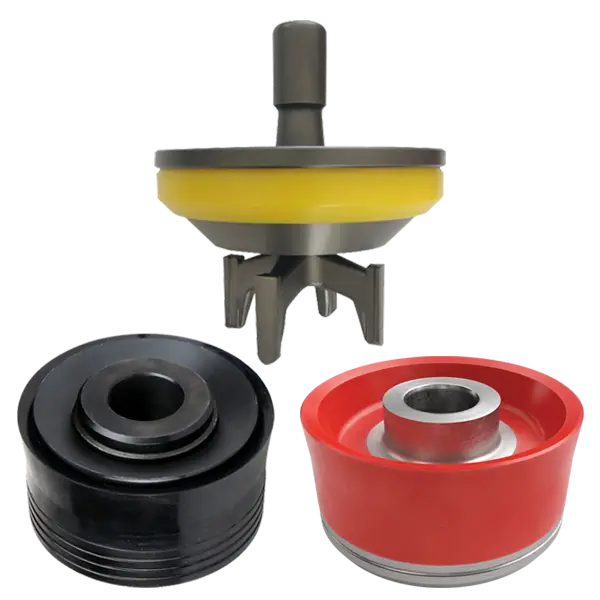

-
BOP Rubber Accessories
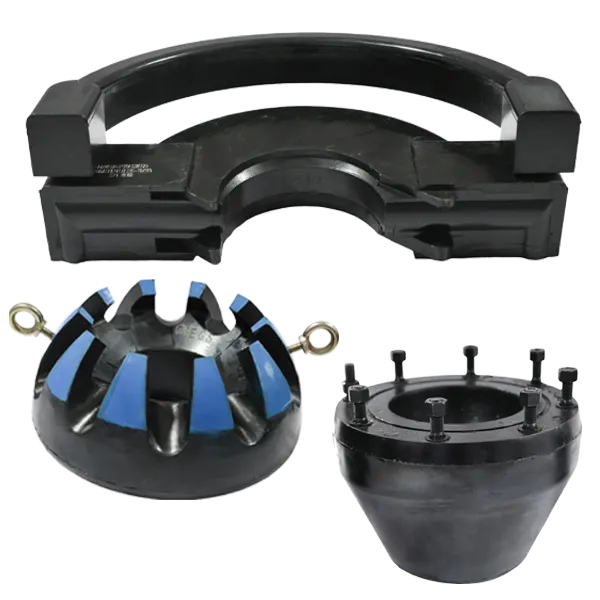

-
Downhole Tool Rubber Components
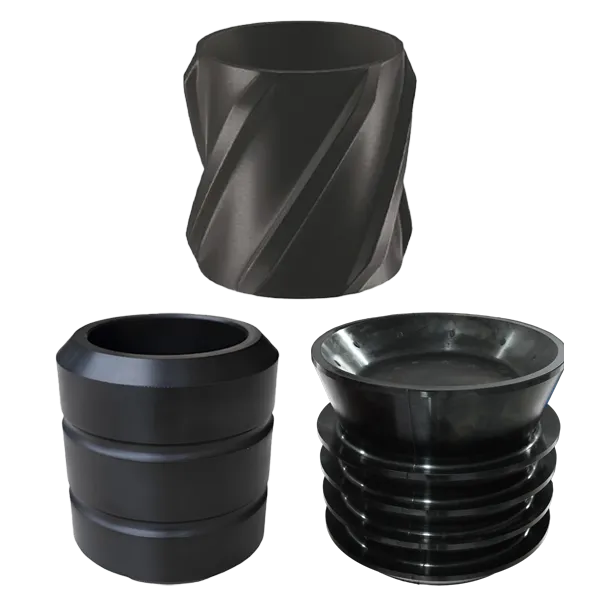

-
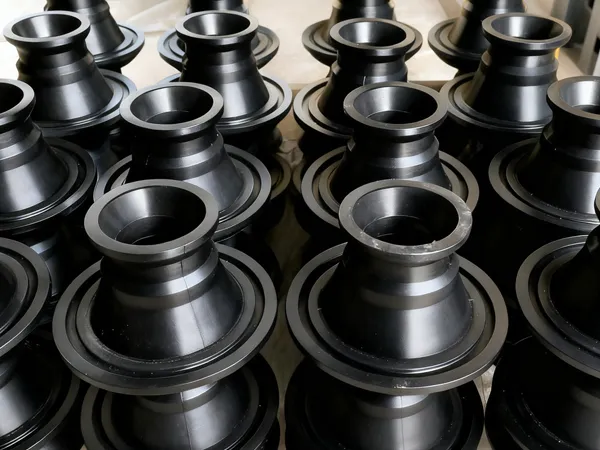
Корпус Централизаторы
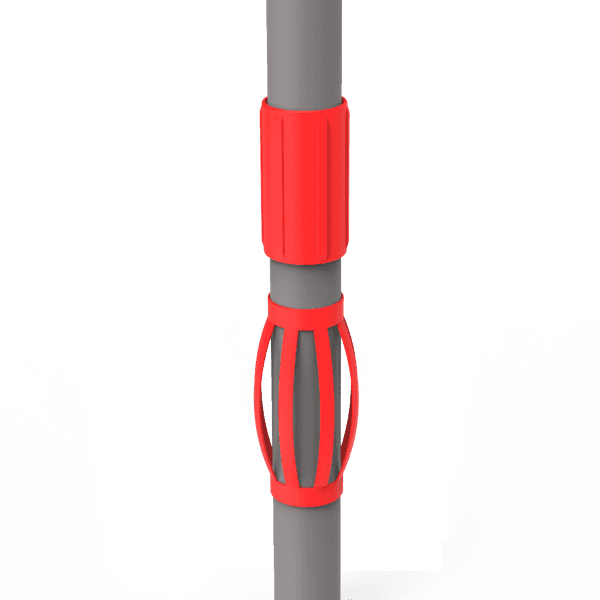
-
Лук Весна Центраторы
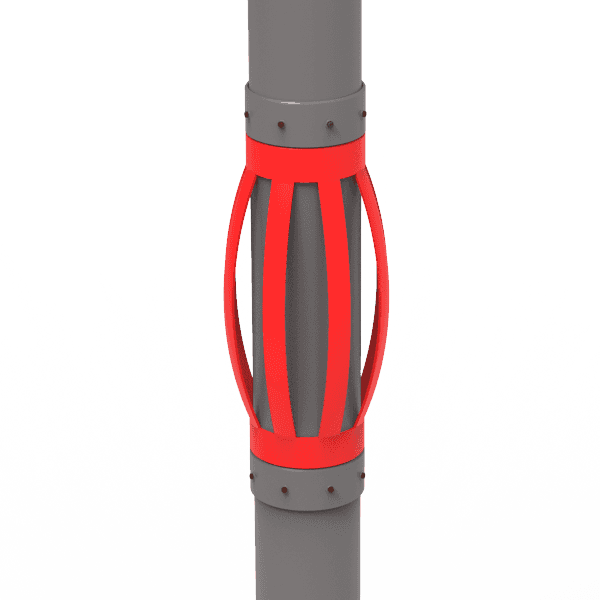
-
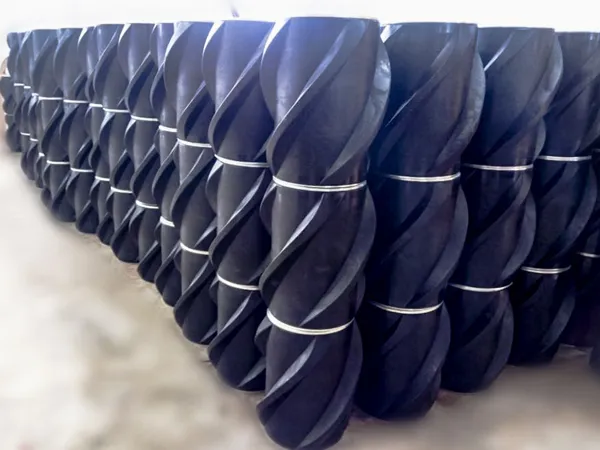
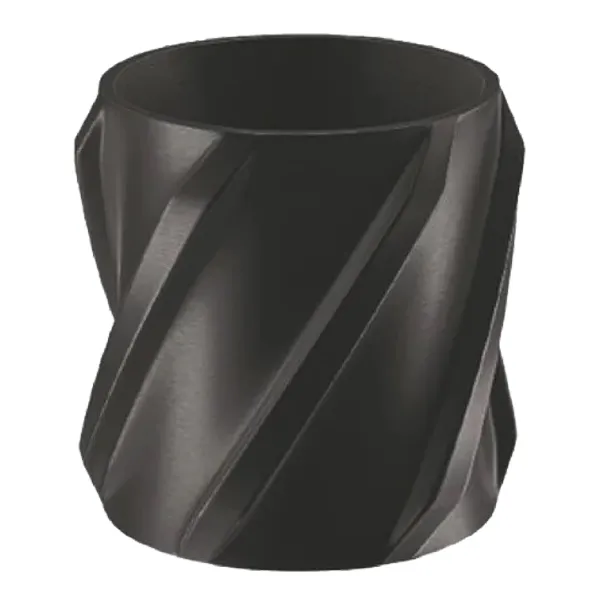
Твердый Жесткий Центр
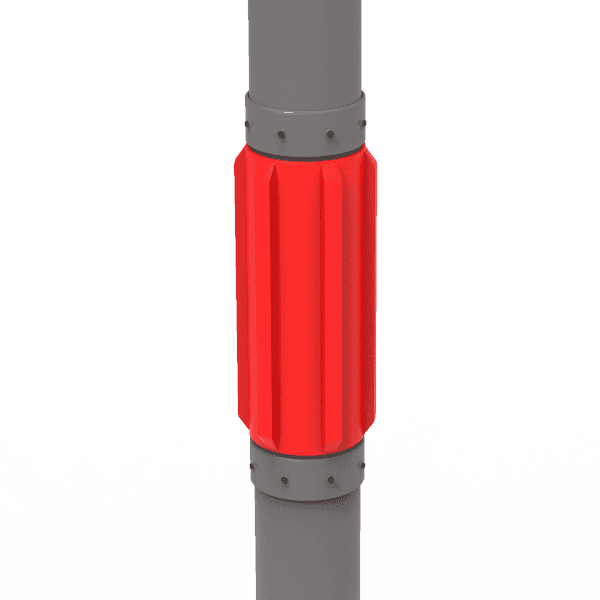
-
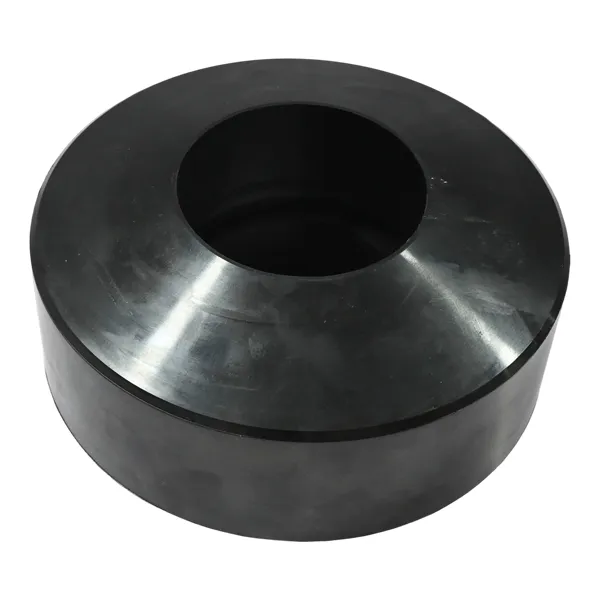
Стоп Воронник
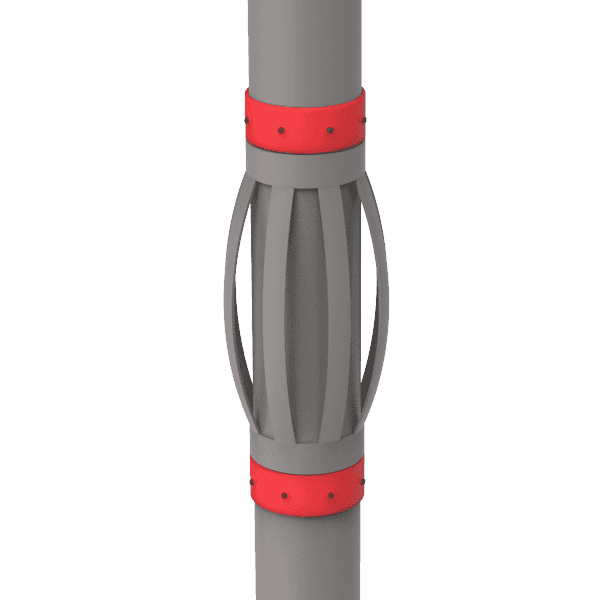
-
Цемент Поплавок Обувь & Воротник
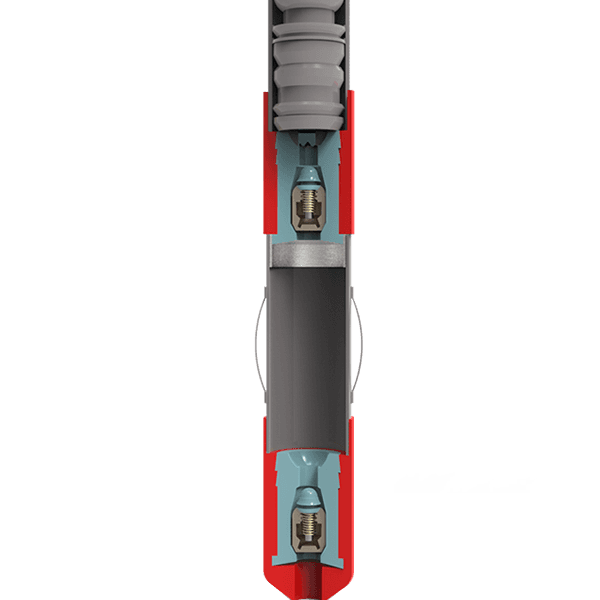
-
Цементировная заглушка
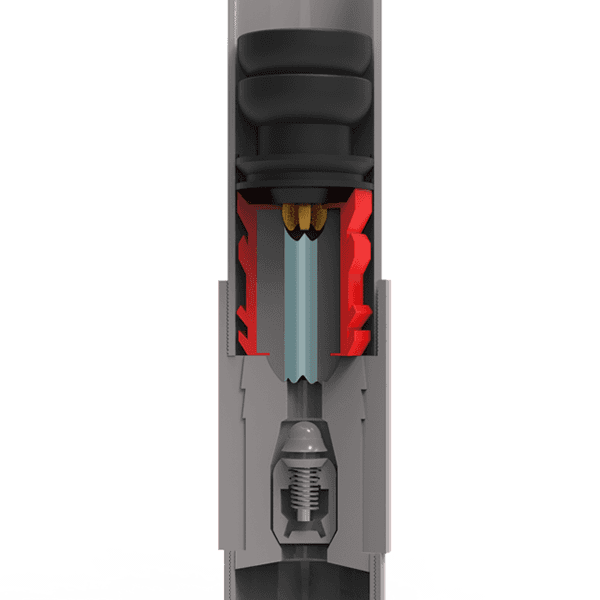
-
Цементировочные корзины
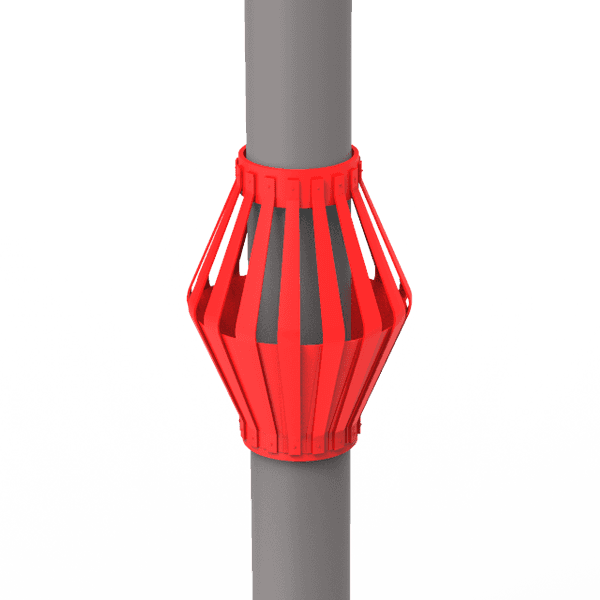
-
Экран бурильной трубы
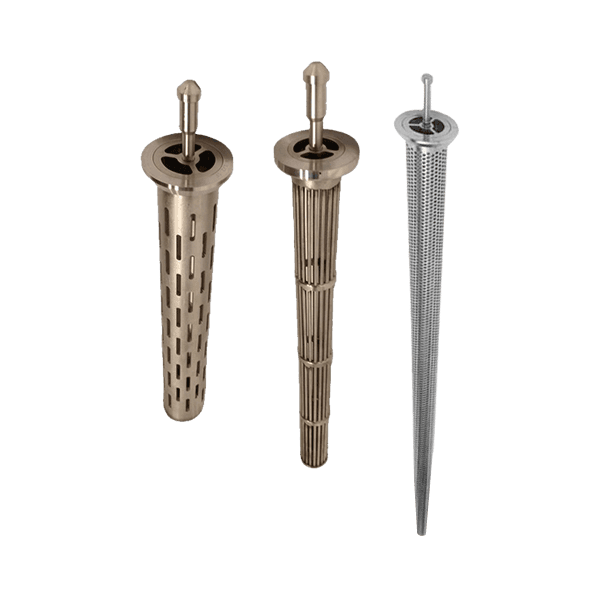
-
Протектор кабеля ЭСП
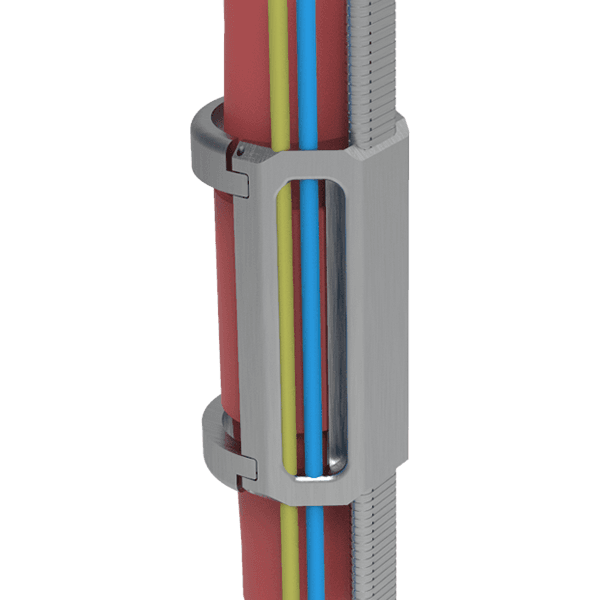
-
Централизатор Присоски СТЕРЖНЯ
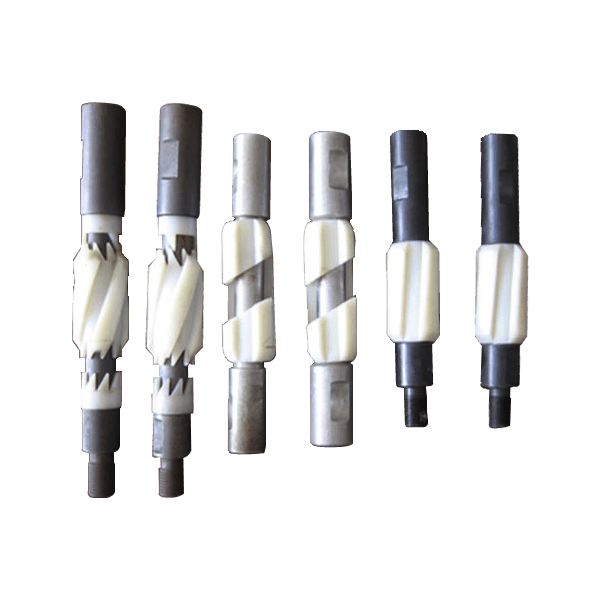

-
Труба обсадной трубы API
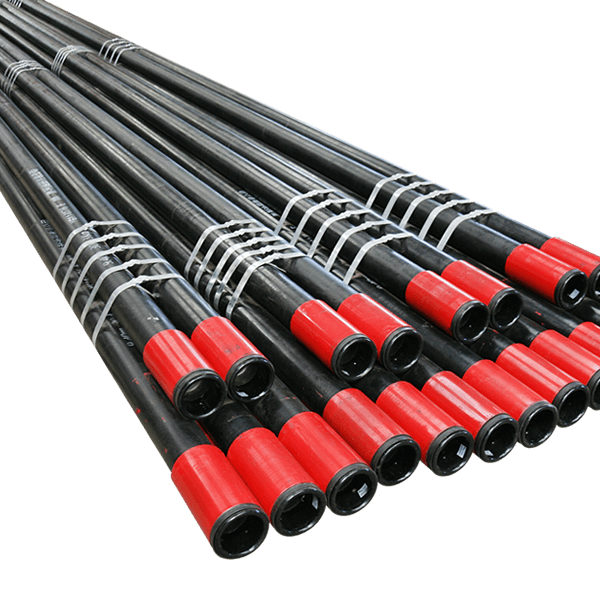
-
Рамки Упаковки Руб

-
СЕТКА ПОКРЫТЯ БЕТОНного ВЕСа (СЕТКА CWC)
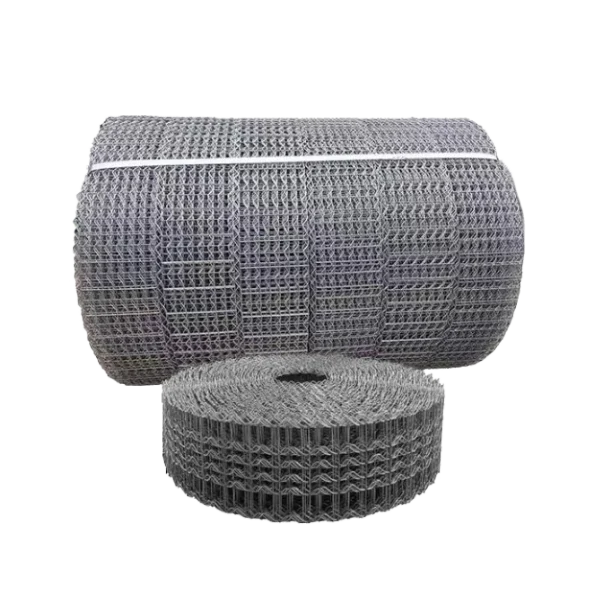

-
Экран провода клина

-
Системы очистки буровой жидкости
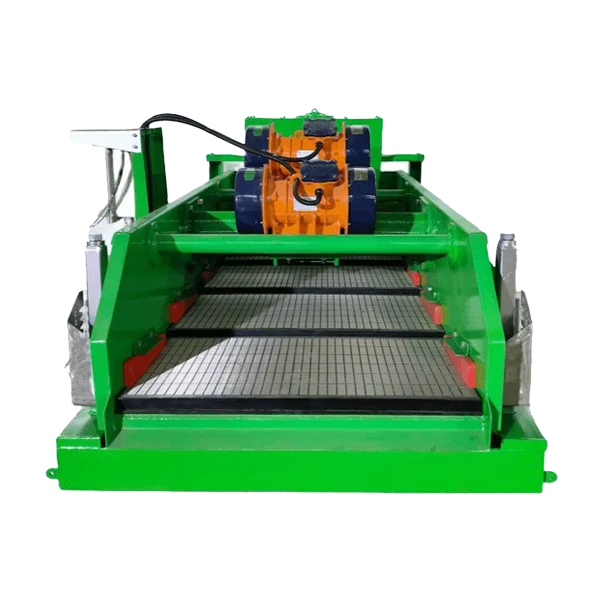

-
Вспомогательное оборудование для очистки буровой жидкости
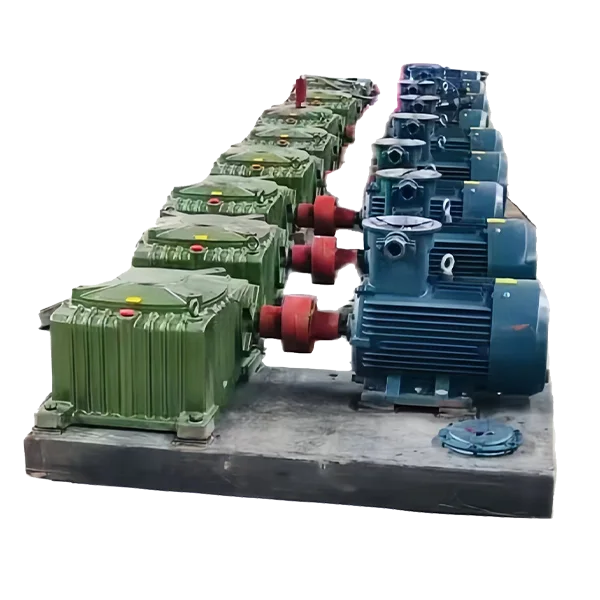

-
- Сервис
- Производство
- О нас
- Контакт
- Главная
-
Продукция
- Протектор резьбы API
- Mud Pump Accessories
- BOP Rubber Accessories
- Downhole Tool Rubber Components
- Корпус Централизаторы
- Лук Весна Центраторы
- Твердый Жесткий Центр
- Стоп Воронник
- Цемент Поплавок Обувь & Воротник
- Цементировная заглушка
- Цементировочные корзины
- Экран бурильной трубы
- Протектор кабеля ЭСП
- Централизатор Присоски СТЕРЖНЯ
- Труба обсадной трубы API
- Рамки Упаковки Руб
- СЕТКА ПОКРЫТЯ БЕТОНного ВЕСа (СЕТКА CWC)
- Экран провода клина
- Системы очистки буровой жидкости
- Вспомогательное оборудование для очистки буровой жидкости
- Сервис
- Производство
- О нас
- Контакт